 In business, one of the fundamental measures of success is the ability to build long-term, profitable relationships. These profits are not necessarily a reflection of just dollars and cents. Relationships can be profitable by measure of intangible assets, such as knowledge, experience, goodwill, association and reputation.
In business, one of the fundamental measures of success is the ability to build long-term, profitable relationships. These profits are not necessarily a reflection of just dollars and cents. Relationships can be profitable by measure of intangible assets, such as knowledge, experience, goodwill, association and reputation.
Businesses and societies are created, built and sustained by people working together towards common goals. It is often equally important in driving towards these goals to rely on who you know, in addition to what you know.
In the quest for driving toward optimal outcomes in any relationship, valuable connections begin by passing the initial test of making a good first impression. These early encounters are often evaluated by a person’s conformity to cultural norms and social graces.
DEFINITION: Social graces are skills used to interact politely in social situations. They include manners and etiquette, which are specifically accepted rules within a culture for the application of universal manners.
It is from these initial first impressions, by chance or circumstance, where relationships are built or discarded. The best foot forward in developing a solid partnership requires a foundation of mutual trust and respect. How that evolves, is through a continuation of good communications, transparency and honesty.
“The most important thing in communication is hearing what isn’t said.” Peter Drucker
Adhering to good business etiquette and social graces helps to open doors and keeps them open. Here are some tips and goals for making the best first impression and building treasured relationships that last a lifetime.
9 Social Graces that Impact Business Relationships
#1: Listen Up. It is critical to be a better listener than talker. Listening is one of the hardest skills to master in life. Our brains are wired to always be on, sifting through new ideas, making opinions and calculating our next move. It takes practice to “manage” all of that activity and just listen. It doesn’t mean you have to be silent. Social graces remind us to pay attention, don’t interrupt and let others speak. First impressions are often based on our ability to listen. Read more on this topic in Listen Up or Lose Out.
Goal: Be a Better Listener.
#2: Make Eye Contact. The inability to make eye contact is probably what loses more people’s interest in the first 10 seconds than any other social grace. Maintaining eye contact in direct communications shows you are interested in what the other person is saying. Be careful not to make it awkward or stare. Not all first contacts are made face-to-face; however, a good tip is to assume they are watching you through whatever device you are using. Imagine they can see where you are looking and how well you are paying attention. Sit up, focus on the conversation and talk directly into the speaker. Eliminate all distractions.
Goal: Give Everyone Your Full Attention.
“Looking someone directly in the eyes during a conversation is the key to making any social or professional connection. We rely on eye contact to communicate and connect with one another on a conscious and unconscious level.” – Psychology Today
#3: Be On Time. Provide the best opportunity for making a great first impression by being on time. Aim for five minutes early in all cases. Being on time is the most costly way to lose opportunities and harm relationships, even before they start. Every second you leave someone waiting is a second they are building up another reason why they are not interested in what you have to say. This applies to meetings over the phone, online or in-person. Being on time shows respect and that you care about the relationship.
Goal: Be the First to Arrive.
#4: Remember Names. It’s all in a name. If you show the lack of attention to remember a person’s name, you probably will lack the attention to detail required to achieve the goals in the relationship. Paying attention during introductions, writing down a person’s name and collecting their information are critical for fostering any relationship. You are better asking someone to repeat their name, then calling them the wrong name or calling them the generic “you” because you neglected to remember their name.
Goal: Get the Name Right.
#5: Ignore Hearsay. We all know how important it is to not judge others. There are many that find their lot in life to influence others with their opinions or share idle hearsay. It is not acceptable for justifying why you do or do not engage in a business relationship. In leadership, one of the biggest mistakes you can make is listening to gossip, chatter, noise and other’s unsolicited judgments in lieu of gathering your own facts and making your own first impressions. He said, she said, they said has no place in business. This does not mean you ignore fair and critical input, it simply means to use “facts” and your own experiences to determine the value in your potential relationship.
Goal: Get the Facts.
#6: Pass on Aggressive. One sure way to prevent any relationship from moving forward is being passive-aggressive. It is probably the #1 business communications violation. This doesn’t mean you should not speak up or participate in the conversation. In fact, not purposely withholding or participating in the conversation can also be a passive-aggressive behavior. Eliminate conversation roadblocks, such as: talking over people, negativity, ‘mansplaining’, interrupting others or giving back-handed compliments. When you begin a sentence, “You always…,” you have entered the danger zone. “Just kidding,” tells others you probably meant exactly what you said. Explaining the obvious is one way to shut down any 2-way dialogue. Aggressive has no place in social graces.
Goal: Avoid Stubborn ‘Know How’
#7: Understand the Culture. We are global. Relationships form at the bases of cultural differences and acceptance. We all have something to offer. This requires awareness and knowledge of cultural norms, behaviors and expectations. Cultures can be defined by demographic and sociographic boundaries like geography, language, heritage and ethnicity. It is also important to recognize that there are cultures within businesses as well. Do your homework in advance. Are gifts acceptable? Do you present a business card? In what direction? Do you use a title? What is the best attire? Ask others who are native to the culture, read, research and use Google. Ignoring cultural social graces when they venture outside your own “world” displays a lack of care and willingness to develop good relationships. It’s ignorant. Respect others and how they do business to get the most out of your relationship.
Goal: Understand the Cultural Impact
#8: Acknowledge and Respect. You never know who you will meet in life and how that person can change your future. The guy in the old pick-up truck driving down the road in Omaha might just be one of the richest people in the world, imagine that chance encounter to develop a meaningful relationship! Being open to other’s ideas, listening to their stories, being present when the ask for your attention are all vital social graces to building good relationships.
Goal: You Can Learn from Everyone
“I speak to everyone in the same way, whether he is the garbage man or the president of the university.”– Albert Einstein
#9: Thank You Matters Most. Two of the most important words in any relationship are thank you. Taking nothing for granted and respecting others time and space, all can be summarized with a note of gratitude. Thank you. Thank you for taking the time to meet. Thank you for your follow-up. Thank you for reaching out. Thank you for the introduction. Thank you for your consideration. Thank you for your help. Perhaps the outcome will not give you what you had hoped when you first engaged with a person; however, how you show up and pay your respect will be remembered forever. Acknowledging others actions shows you care and that is the ultimate social grace.
Goal: Always Give Thanks!
Thank you for taking the time to read this post. I look forward to staying connected and continuing the conversation.
Jamie Glass, CMO + President of Artful Thinkers, a sales and marketing consulting company.











































 What works in business is “doing”. Executing the plan requires effort. It is the muscle, the labor and the heavy lifting that gets the job done.
What works in business is “doing”. Executing the plan requires effort. It is the muscle, the labor and the heavy lifting that gets the job done.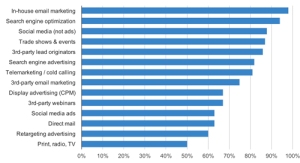
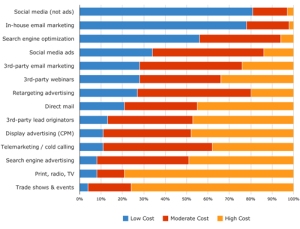
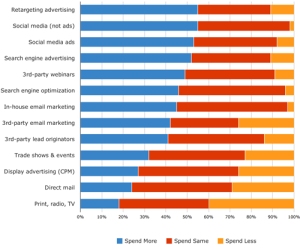












 As a business leader, you have three options of where to put your focus. The Past. The Future. The Now. Being present in your business now, gives you better leverage to improve from your past with the valuable foresight to manage risks and opportunities in your future.
As a business leader, you have three options of where to put your focus. The Past. The Future. The Now. Being present in your business now, gives you better leverage to improve from your past with the valuable foresight to manage risks and opportunities in your future.






















You must be logged in to post a comment.